Viral metagenome, also known as Virome, is a new branch of discipline based on the theory of metagenomics and combined with existing virology and molecular biology techniques.
Macrovirome breaks through the limitations of traditional technical methods, directly takes the genetic material of all viruses in the environment or organization as the research object, and can quickly and accurately identify all virus components in the sample, which is a powerful means to discover new viruses, study the structure and diversity of viral populations, monitor virus mutation and evolutionary research. It plays an important role in virus discovery, virus traceability, and microbial early warning.
Future Research Trends
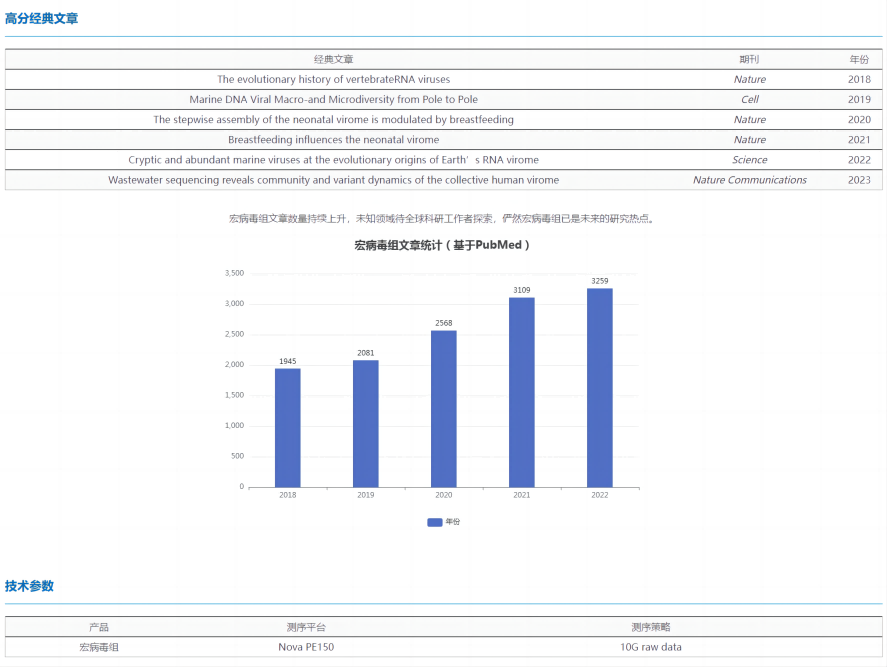
In recent years, many high-scoring articles on the macrovirome have been published, including soil, water and human body, which shows that the macrovirome has attracted the attention of researchers from all walks of life, and as the goal of follow-up research, the so-called "small viruses are everywhere; The virus has a great future!"
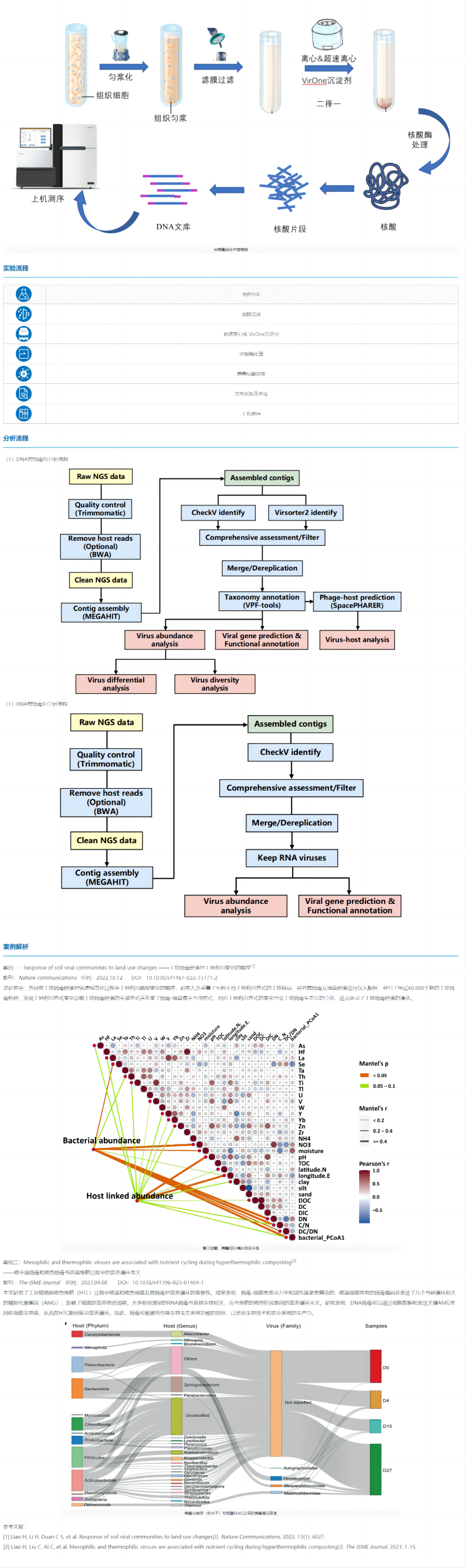
Technical route
Viruses are ubiquitous, but in human tissues, oceans, or soil samples, viruses are low in content due to their small genomes, and host components are difficult to remove in complex samples, so viral enrichment is a problem for the macrovirome. The scientific R&D team of Zhongtian Vaineng has developed two efficient virus enrichment solutions to help researchers overcome difficulties and accelerate the research process of macrovirome!
Ultracentrifugation: With the help of an ultracentrifuge, the sucrose density gradient centrifugation of the preliminarily filtered sample for more than 24 hours can effectively separate the virus particles in the sample from prokaryotes and cell debris.
VirOne Competitive Precipitation: The original VirOne competitive precipitation method competitively binds water molecules and neutralizes surface charges, forcing VLPs to precipitate from solution and rapidly collecting viral particle pellets by conventional centrifugation.
Both of the above schemes have been tested by a large number of samples, which can greatly increase the proportion of effective virus data in the sequencing data, and provide a reliable guarantee for the subsequent analysis results.